The Owl (and others)
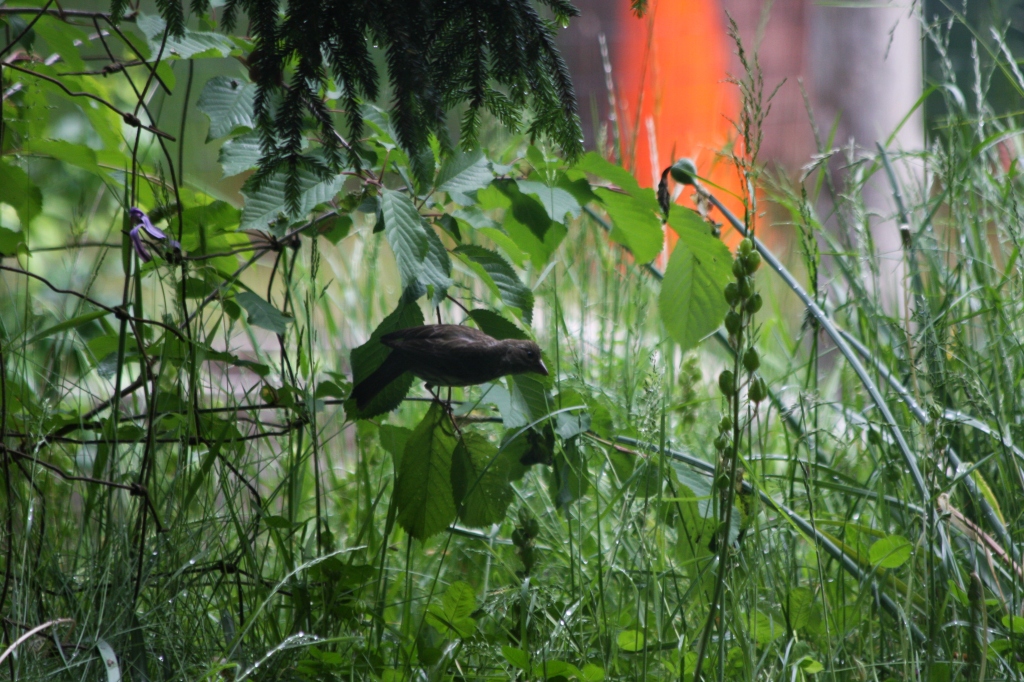
Today was a day of bird encounters. I saw our poor little cowbird that can’t fly because he’s been injured (likely by our neighbor’s marauding outdoor cat). He’s survived three nights so far even though he seems to have a wing injury and I haven’t figured out yet if I can capture him to check. He’s had his little mate following him around.

I know it’s a cowbird and cowbirds are brood parasites, but they are actually quite beautiful little birds and I feel sympathy for wildlife that are impacted by our human “pets.” It isn’t fair and we should do much better to keep our pets under control. I don’t know what my response would be if I see this cat attacking our Tanager or one of the Grosbeaks. It is doing what cats do and the problem isn’t the cat, but the owner who evidently doesn’t care and is probably too lazy to clean a litter box and play with the cat and keep it inside. Ok. So, I vented. Sigh…
I was going out to take a walk in nature to unwind when I heard a sad little thunk on our window. We have Acopian Bird Savers https://www.birdsavers.com/make-your-own/ on the largest window, but not the smaller one. That’s gonna change. I’m going to put them on ALL our windows.
Well, I looked out and saw a tiny little nuthatch on the ground, on its back, mouth open, but it was breathing. I ran out to pick it up and when I scooped that little creature into my hand, its feet wrapped around my finger so tightly that I felt hopeful. It was a newly fledged nuthatch. I sat with it quietly in the shade under the suet feeder, my hand stretched out onto my knee into a little cup shape.
The bird closed its eyes and slept a bit. I talked to it very very softly. An adult nuthatch landed on the feeder above, eyeing me cautiously. I believe it was the parent. I spoke to the adult too, trying to convey my earnest intent not to harm her child. The little one blinked and looked about. Then it closed its eyes and slept a bit again. The parent flew over to the fruitless cherry tree to another feeder, then off, I expect to feed another hungry mouth.
After a good 15 minutes, the little nuthatch was much more alert. It kept eyeing the suet feeder and the adult bird that returned again and again. I rose slowly from sitting, carefully supporting the little one – still gripping my finger. Raising my arm, I chose a small branch just beside the suet feeder and in a breath, the little one hopped off my finger and onto the new perch.

The adult nuthatch flew onto a nearby branch and I saw the fledgling flutter its little wings like baby birds do to get their parents’ attention to be fed. In another breath, it was airborne, flying after the parent. I was so grateful for a happy end to that incident.
My walk down our road was uneventful for the most part. I did see a Clown millipede (Harpahe crossing the wetland area and squatted down to observe its somewhat awkward, but systematic locomotion. It almost looks suspended in motion over the ground. After making sure it was safely out of harm’s way and not in a car path, I continued on.
My destination was the “soon to open officially” nature preserve. I have walked on this property for about 10 years now. It is an amazing place.
Giant cedars tower overhead through the wetland. Along the seasonal stream, the path I took meanders amidst the primordial assortment of ferns, swamp lanterns, and horsetail. There are creatures there in the forest. If you see them, you will leave feeling a sense of awe.

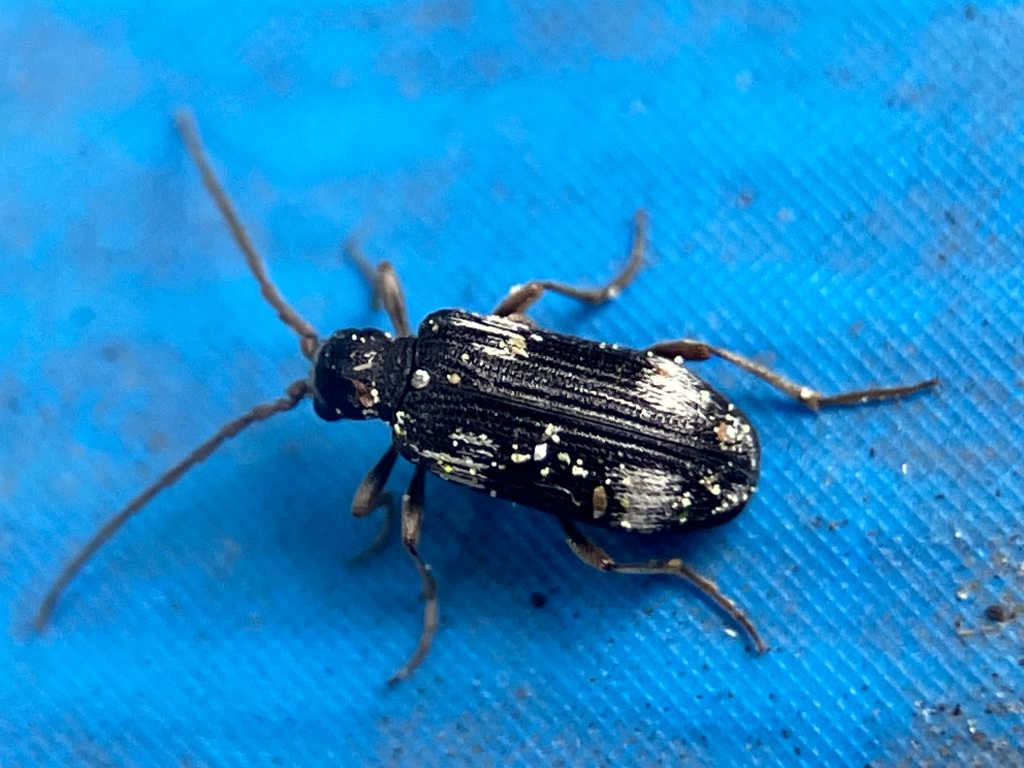
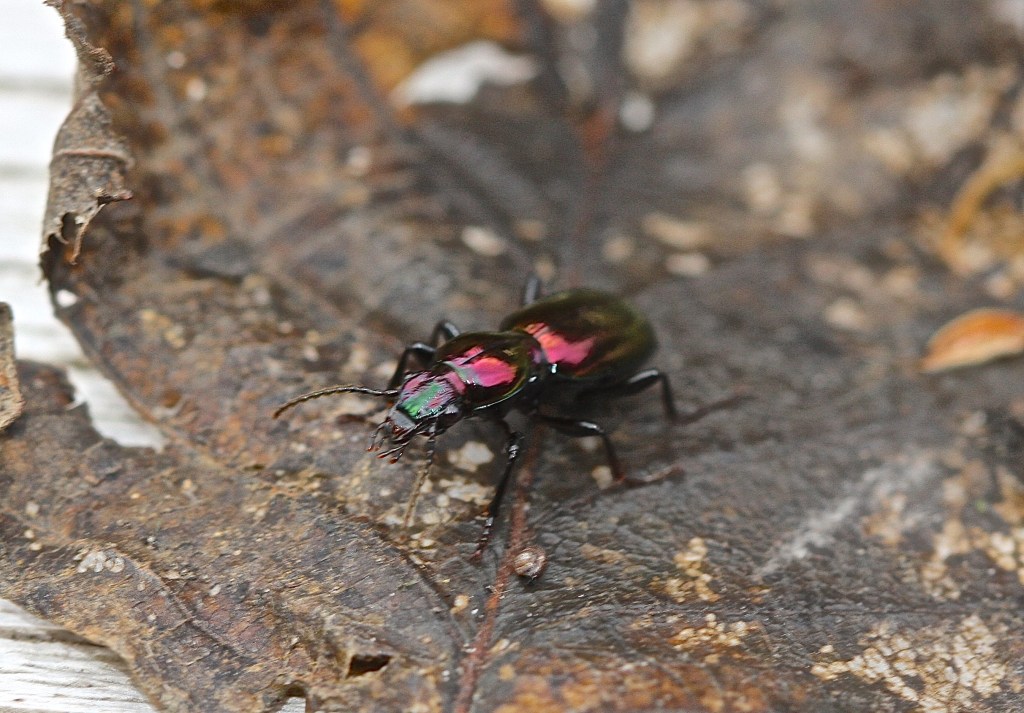
Red legged frogs, salamanders, and newts make their homes in the wetland. They dine on the myriad of invertebrates that live in the stream and mud. On the forest floor, you’ll find Night-stalking tiger beetles (Omus dejeanii) with fierce jaws hunting for prey. If you’re really really lucky, you might see the burgundy metallic carabid beetle (Zacotus matthewsii) that I’ve only seen less than a handful of times in the past decade. Overhead, you’ll hear the family of ravens that have a nearby nest. Always in the same place.



The hawks hunt in a small clearing where the stream attracts other animals that come for a drink. There are other birds hidden too. Flycatchers nesting in rotting snags, Pileated Woodpeckers drilling after carpenter ants. And the owl.

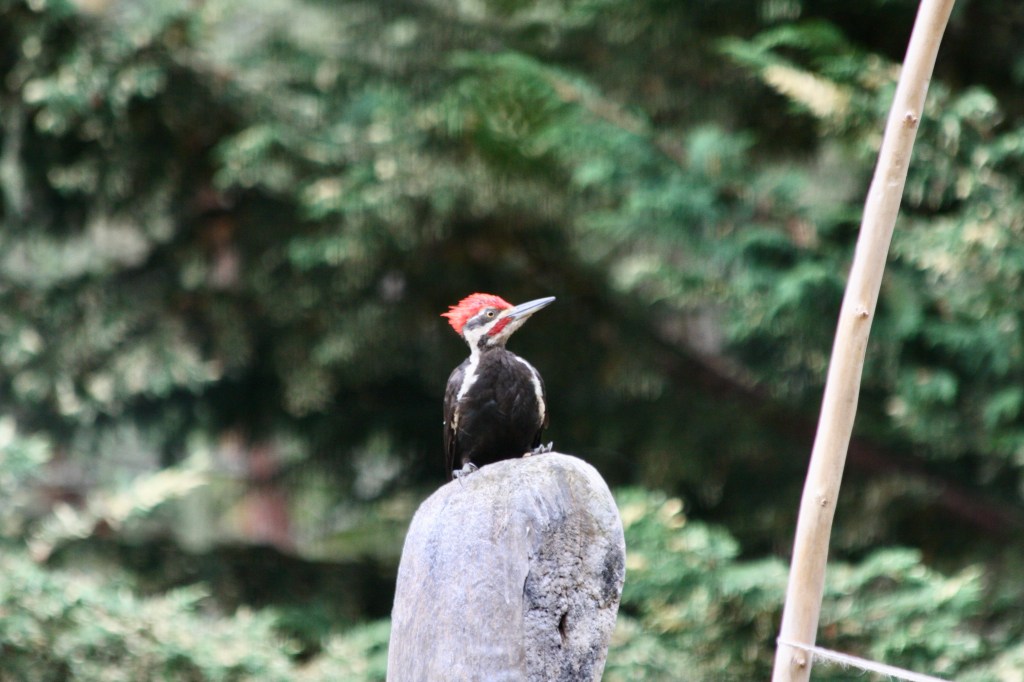
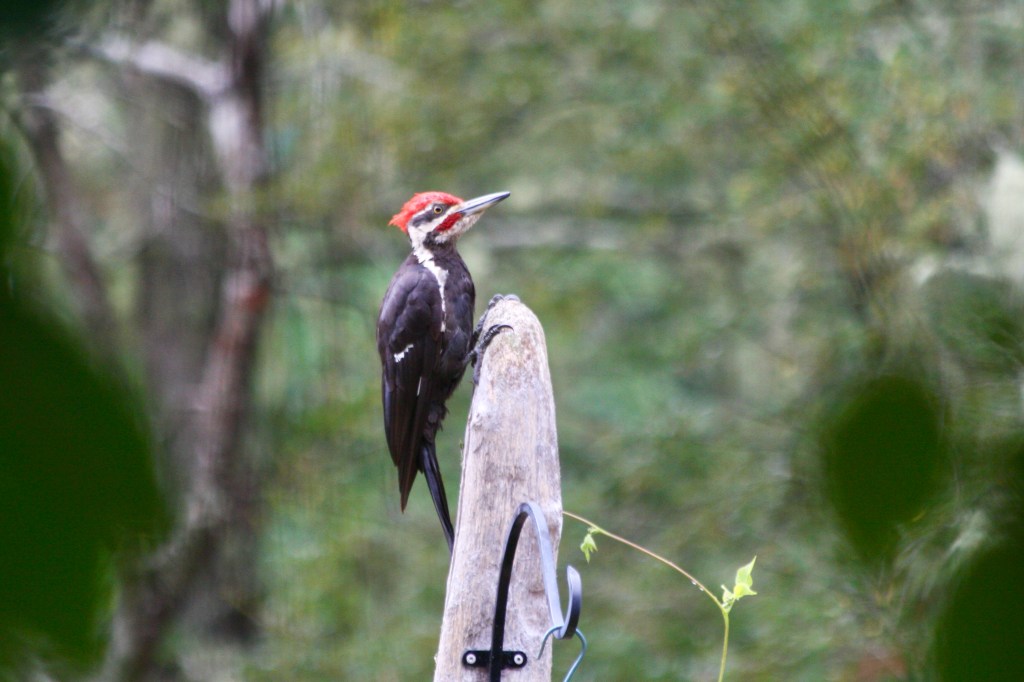
The owl has been there for a long time. You can hear it calling in the night – “Who Cooks for You?” It was wonderful before there were too many houses. Now, it is harder and harder to hear the owl over the din of barking dogs. In the woods though, the owl has a baby.
I heard it calling the other day. Screeching is more like it. I heard the noise before saw them. The mother owl was watching me cautiously from high above. A snake dangled from her mouth. In spite of this, I heard her utter sounds of caution to her child. She flew over to feed it as I quietly backed out of the area. I did not want to disrupt them and when I walk, I try always to remember that I am entering the home of others. I walk quietly and respect their spaces.
Today, when I walked back to the place of the owl, I heard the baby again. It was calling repeatedly, but mom was nowhere to be seen. Again, I backed away quietly, hoping the owl was able to find food for her little one. They must hunt through the day and not only at night in order to rear their offspring.
I thought of the owl as I walked back to the trailhead and then I momentarily became distracted as I reached the site where I’d been poking around in a raccoon carcass on the trail. There are some very cool bugs that you find in carrion. Unfortunately, the remains were not to be found.
Stepping off the trail to look in the underbrush for any sign of the carcass, I heard a flutter overhead. I looked up and she was there. It was the mother owl.
She landed on a branch right in front of me. I was too dumbfounded to move. We stayed like that for what seemed like a very long minute. She gazed at me and I watched her in turn, not daring to blink. There was no threat. I felt like she knew me.
The robins were not happy and began to flail at her, creating a cacophony of rebuke. She ignored them. I slowly brought my phone around and took a video of her. She just looked at me.
Then she looked around, gazing through the forest at things unseen. After about five minutes, she reoriented her body, turning away from me, surveying the surrounding area. With a glance back at me, she flew away.
This encounter is why saving spaces for WILDLIFE is so incredibly important to me. These places should belong to them. When we visit a preserve, remember that. It is their home.
I hope others will reflect on what I’ve shared, and maybe there will be one less person who lets their dog off leash or one less person who throws trash onto the forest floor. Think about the creatures that call these places home. Walk softly and be respectful of their need and struggle to survive in ever-shrinking spaces.
Thank you for reading. Support Conservation. Save Spaces for Nature.