Louse in the House


Hmmm, I was trying to think of a catchy title. “Louse in the House” made you look, right? Well, indeed one did escape and I can’t find it. Would you like to come over for dinner tonight? I thought I saw it flying around the dining room.
Here’s how it happened. Yesterday afternoon, a bird hit the window. It was a hard strike on a window where we haven’t had many bird collisions. I suppose I’ll have to make more Acopian Bird Blinds to put up. They’ve sure help mitigate the bird strikes. Link to DIY instructions here: https://www.birdsavers.com/make-your-own/
Back to the bird. I went out to see if the poor bird was still alive. It was, but died in my hands soon after I picked it up and carried it into the house to assess for injuries. I took the bird into the bathroom so I could shut out my ever-curious indoor cats, Herman and Nimbus. After realizing I was holding a lifeless body, I set the bird down in the bathtub. Right away, I noticed a fly crawling through the bird’s feathers. Hurriedly, I left the bathroom, grabbed my camera, and went back to examine my specimen more closely.

As I bent over to look through the feathers, a fly zoomed up and nearly entered my nostril. I backed away, rubbing my nose. Wouldn’t be my first strange experience with a fly. There was that incident with the botfly that could have been a medical ophthalmological emergency. Don’t ask. You truly don’t want to know.

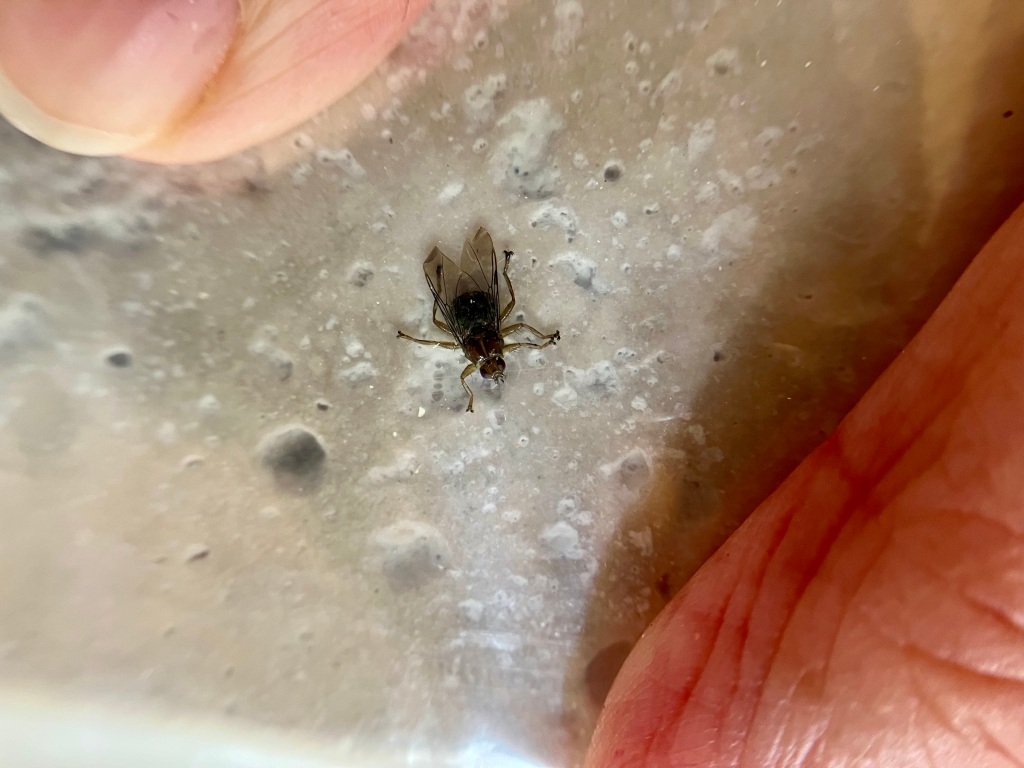
Leaning back over the tub, I started to look through the feathers again, but thought better. I went out of the bathroom again. This time to retrieve a large plastic bag and a collection vial for specimens. The bird went into the clear plastic bag. Now, I could look while containing the flies in the bag if there were others to be found.
I found two more.
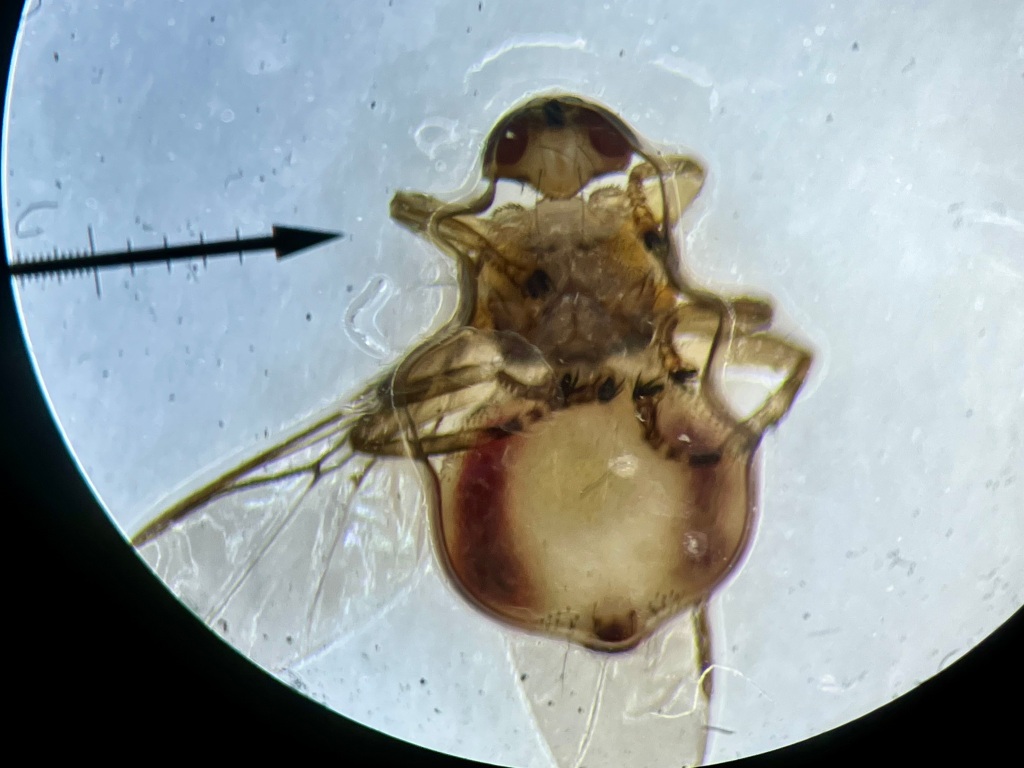
These are Louse Flies in the family Hippoboscidae. The ID for this particular species is Icosta americana. Also, my husband identified the bird as a juvenile Brown Headed Cowbird (Molothrus ater). Strangely, this species is known to be chiefly associated with the bird families Accipitridae (birds of prey – hawks), Phasianidae (pheasants), and Strigidae (owls). So, why might it be on a cowbird? The bizarre exception. Maybe the cowbird parents laid their egg in the nest of one of the above? I suppose it will be a mystery.
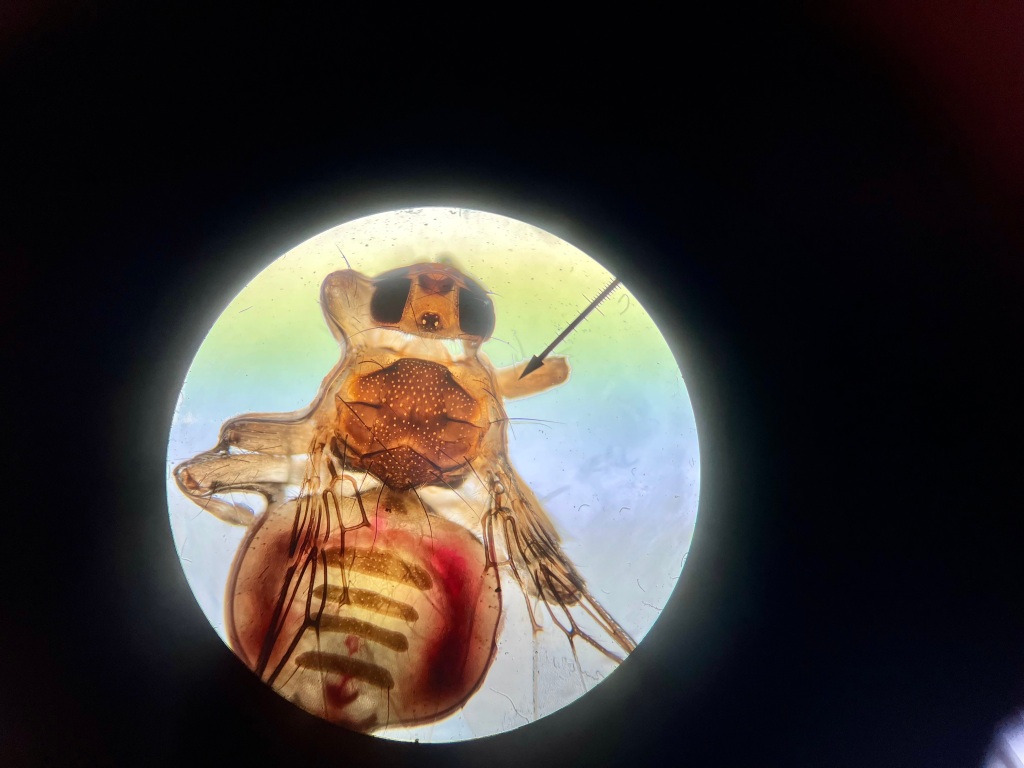
Hippoboscid louse flies are pretty interesting. First off, don’t they look weird? Trust me when I tell you they are one of the most bizarre families of flies out there. They are obligate ectoparasites that feed on the blood of their host, nothing else. Unlike other fly groups, both male and female flies in this family feed exclusively on blood.
There are more than 200 species of Hippoboscid flies, and each species is particular about what sort of host it feeds on. Some feed on sheep, some on deer, others on bats, but the ones I found feed on birds. In fact, approximately 75% of species of Hippoboscid flies are bird parasites. Of these 75%, some are so picky, they only prefer a particular species of bird.
Another interesting thing about these flies is the fact they vector diseases like Avian Malaria, West Nile virus, and various Trypanosomes among the host species they parasitize. Unlike some other Hippoboscid species which have deciduous wings (wings that are quickly lost when reaching a host), the ones that parasitize birds can fly during their entire adult life. This means if their host dies, like my bird that hit the window, the flies are able to leave the bird’s body and fly off to parasitize another bird host.
While one fly may have attempted to target my nose, these flies are not known to parasitize humans, although incidental bites have been recorded. Some species of female Hippoboscid flies are actually known to only be able to develop their eggs from the blood of their particular host species.

While on a host, Hippoboscid flies move about with ease. They have bodies that are dorso-ventrally flattened, somewhat like an unfed tick body or a squished bug body. In fact, the Hippoboscid flies that parasitize deer are often mistaken for ticks. Because of the flattened body, sometimes these flies are referred to as flat flies. This shape makes it easy for them to glide between fur or feathers, and it also makes it hard for the host to groom them off.
The most remarkable thing about Hippoboscid flies is their reproductive biology. It is known by the term, Adenotrophic viviparity. Adenotrophic viviparity is where eggs hatch inside the female, and the larvae are fed internally until they are mature enough to pupate. In layman lingo, the female fly gives birth to a single live larva just as it is ready to pupate. She has invested all her resources into producing a single offspring.
This is unique as most fly species cast eggs onto a substrate and the eggs hatch into larvae, feed independently of the parent, pupate, and emerge as adults. With Hippoboscid flies, the female parent retains the single egg inside her uterus, the egg hatches into a larva, and she feeds it with special milk glands until the larva reaches the last stage of larval development or “prepuparium.” Finally, the adult fly “births” her offspring larva enclosed in a shell that quickly hardens into a true pupa. With Hippoboscid species that parasitize birds, the adult fly will leave her pupa in a bird’s nest or roosting site where it can easily find a host when emerges as an adult. For more on the life cycle of Hippoboscidae, you can view one of my YouTube videos here – https://youtu.be/zCD1B2GjCxU
*** In case you’re sitting here scratching your head and I wasn’t clear in the text, ALL of the collective names for Hippoboscid Flies include the following: Flat Fly, Louse Fly, Ked Fly, or just plain ole Ked. And yes, they ARE known to have a painful bite!
References and Further Reading
Coatney, G. R. (1931). On the Biology of the Pigeon Fly, Pseudolynchia maura Bigot (Diptera, Hippoboscidae). Parasitology, 23(04), 525.
Dick, C.W. 2006. Checklist of world Hippoboscidae (Diptera: Hippoboscoidea); Department of Zoology, Field Museum of Natural History: Chicago, IL, USA, pp. 1–7.
Levesque-Beaudin, V. Sinclair, B.J. 2021. Louse fly (Diptera, Hippoboscidae) associations with raptors in southern Canada, with new North American and European records. International Journal for Parasitology: Parasites and Wildlife,
16: 168-174. ISSN 2213-2244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijppaw.2021.09.007
Maa, T. C. 1969. a Revised Checklist & Concise Host Index of Hippoboscidae (Diptera). Pacific Insects Monog., Honolulu: Bishop Museum, Honolulu, Hawaii. 20: 261–299. http://hbs.bishopmuseum.org/fiji/pdf/maa1969b.pdf
Santolíková,A.;Brzonˇová, J.;Cˇepicˇka,I.;Svobodová,M. 2022. Avian Louse Flies and Their Trypanosomes: New Vectors, New Lineages and Host–Parasite Associations. Microorganisms. 10, 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/ microorganisms10030584
Small RW. 2005. A review of Melophagus ovinus (L.), the sheep ked. Vet Parasitol. 130(1–2):141–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2005.03.005 PMID: 15893081
Walker, Meredith Swett 2015. Behold the Hippoboscidae: Bizarre Biting Flies that Give Live Birth! Entomology Today. https://entomologytoday.org/2015/05/18/hippoboscidae-flies-live-birth/

That was fascinating, Cynthia! Thanks!
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thank you Dan!
LikeLiked by 1 person